The National Institutes of Health in 2021 published Exosomal Therapy—A New Frontier in Regenerative Medicine which stated:
“… exosomal therapy has now been transformed into a potential platform with immense promise for future therapeutics.”
But what exactly are exosomes, and why are they sparking interest in medicine and biology? Explore exosomes’ groundbreaking therapy for regenerative medicine. Join our journey toward healing and hope.
What are Exosomes?
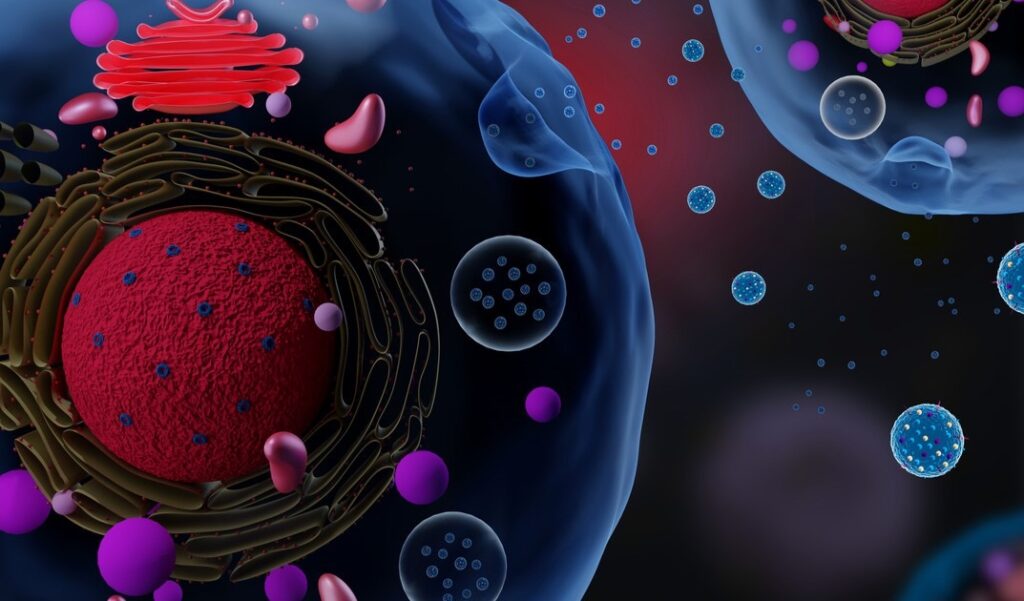
Exosomes are tiny vesicles or structures that cells release into their surrounding environment. Exosomes facilitate cell-to-cell communication and transport various molecules, including proteins, lipids, RNA, and DNA.
Think of exosomes as messengers that cells use to communicate with each other over short and long distances. All cell types in the body can release exosomes, which play essential roles in various biological processes, including immune response, tissue repair, and development.
What is Exosome Therapy?
Exosome therapy, also known as exosome-based therapy or regenerative medicine, involves using exosomes as therapeutic agents to treat various diseases and conditions. Cells naturally release exosomes that transfer bioactive molecules* and participate in cell-to-cell communication.
* Bioactive molecules are substances found in nature that specifically affect living organisms. These molecules interact with biological systems, such as cells, tissues, or organs, and can influence various physiological processes. They can have diverse roles, including regulating cellular functions, promoting health, or exerting therapeutic effects.
Bioactive molecules are like the ingredients in nature’s toolkit that can affect how living things function and feel. They exist in foods, plants, and our bodies and are essential in keeping us healthy and functioning correctly.
Overview of How Exosome Therapy Works
Isolation and Purification
We can isolate and purify Exosomes from different cell sources, such as mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)*, immune cells, or other specialized cell types. The isolation process typically involves centrifugation and filtration techniques to separate exosomes from other cellular components and debris. The isolation process typically involves centrifugation and filtration techniques to separate exosomes from other cellular components and debris.
*MSCs are cells found in the body, often in bone marrow, fat tissue, and other connective tissues. They have a unique ability to transform into different types of cells, such as bone cells, cartilage cells, and fat cells. MSCs also produce various substances that can help reduce inflammation and support tissue repair. Think of them as the body’s repair crew—they can change into different cell types as needed and release helpful substances to heal damaged tissues.
Characterization
Once isolated, we confirm the exosome’s identity and purity. This process involves analyzing exosomes to ensure they meet the quality requirements for therapeutic use. We analyze their size, shape, protein markers, nucleic acid content (molecules that store and transmit genetic information), and other characteristics.
Therapeutic Loading
Think of exosomes as tiny delivery vehicles; “loading” them is like packing them with cargo, such as therapeutic drugs or molecules. Just as you might load a truck with goods for delivery, loading exosomes involves incorporating specific substances or molecules into their structure. This process allows us to customize exosomes with desired cargo, enhancing their ability to deliver therapeutic agents to target cells or tissues in the body. This loading process aims to improve the therapeutic potential of exosomes by delivering specific molecules to target cells and tissues.
Administration of Exosome Therapy
Exosome therapy involves administering exosomes to the patient. The route of administration can vary depending on the target tissue or disease we are treating. We can administer exosomes via intravenous injection, local injection at the site of injury or disease, inhalation, or other appropriate routes.
Exosome Therapeutic Effects
Once administered, the exosomes exert their therapeutic effects by interacting with recipient cells. The transferred bioactive molecules within exosomes can modulate cellular functions, promote tissue repair and regeneration, modulate immune responses, or influence disease processes.
In other words, they can change or control how cells behave in the body. They can make cells work harder or slower to keep everything in balance or adjust to changes in the surroundings. For instance, modulating cellular function might mean making more specific proteins to help cells grow and fix themselves or slowing down particular processes that cause inflammation or disease. Modulating cellular function helps cells adjust to different situations, keeping everything running smoothly and helping us stay healthy.
Unlocking Youthful Vitality: Exploring Exosome Therapy with Forbes Longevity Center
In conclusion, exosome therapy offers a revolutionary approach to combating the effects of aging at the cellular level. By harnessing the regenerative potential of exosomes, we are unlocking new possibilities for promoting youthful vitality and extending a healthy lifespan. If you’re interested in exploring the potential of exosome therapy for rejuvenating your health and vitality, we invite you to contact Forbes Longevity Center. We are dedicated to guiding you on your journey to optimal wellness using a very personalized approach. Together, let’s embrace the transformative power of exosomes and pave the way for a healthier, more vibrant future.



